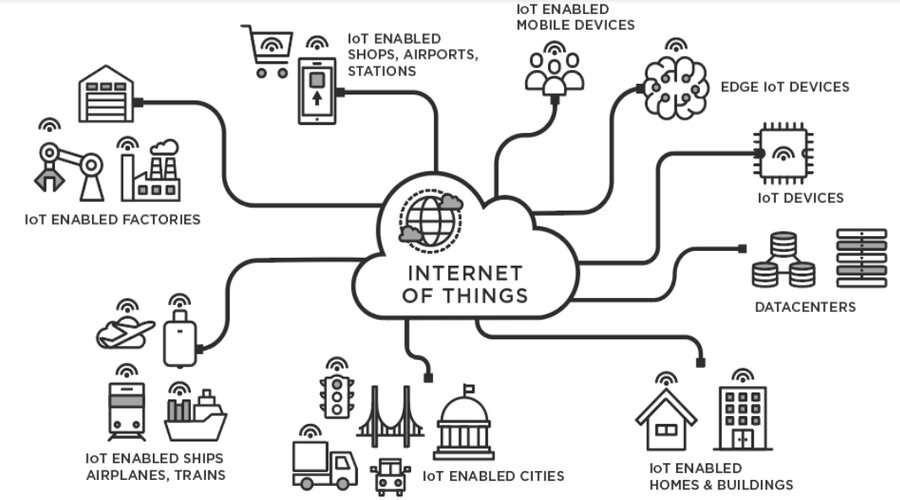
In today’s digital age, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology, revolutionizing the way we interact with our environment. With the ability to connect various devices and systems, IoT(Internet of Things) opens up a world of possibilities, enabling seamless communication, automation, and data-driven decision-making. In this article, we will delve into the exciting world of IoT, exploring its applications, benefits, and challenges.
What is IoT(Internet of Things)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data over the internet. These devices can range from small wearables to large-scale industrial machinery, creating a vast network of interconnected things.
Taking everyday things, embedding them with electronics, software, sensors and then connecting them to internet and enabling them to collect and exchange data without Human intervention is known as INTERNET OF THINGS(IOT).
History Of Internet of Things
- In 1982, Carnegie Mellon researchers connect a vending machine to internet to remotely check for cold sodas.
- Term “The Internet of Things” (IoT) was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999.
- IN 1990 the first toaster was operated over the net.
- In 2000, LG Introduced first smart fridge.
- In 2004, First smart watch introduced.
- 2007: Apple smart phone and wearable fitbit released.
- 2009: Google starts testing self driven cars.
- 2011: Smart tv Introduced
- 2013: Google lens released.
- 2014: Echo cause a crucial role in smart home market.
- 2015: Tesla comes out with Auto piolot drive for their cars.
The Key Components of IoT:
To understand how IoT(Internet of Things) functions, it’s crucial to grasp its key components, including sensors and actuators, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces.
Sensors and Actuators:
Sensors are vital components of IoT devices as they collect data from the surrounding environment. They can measure various parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressure, light, and motion. Actuators, on the other hand, enable IoT devices to perform actions based on the collected data, such as turning on lights or adjusting room temperature.
Connectivity:
Connectivity forms the backbone of IoT(Internet of Things), allowing devices to communicate and share data with each other. This can be achieved through various wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks.
Data Processing and Analytics:
The massive amount of data generated by IoT(Internet of Things) devices needs to be processed and analyzed to derive meaningful insights. Cloud computing and edge computing play a crucial role in handling and analyzing this data to enable real-time decision-making.
User Interfaces and Applications:
User interfaces and applications provide a way for users to interact with IoT devices and access the collected data. These interfaces can be mobile applications, web portals, or voice-activated assistants that enable seamless control and monitoring of IoT devices.
Applications Across Industries:
IoT(Internet of Things) has immense potential and is being adopted across various sectors to revolutionize operations and deliver advanced services.
Smart Homes and Home Automation:
IoT enables homeowners to control and automate various aspects of their homes, such as lighting, temperature, security systems, and entertainment devices, using their smartphones or voice commands.
Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring:
IoT devices are transforming healthcare by allowing remote patient monitoring, wearable health trackers, and smart medical devices. This technology enhances patient care, enables early detection of health issues, and reduces hospital visits.
Industrial IoT (IIoT):
In industries, IoT(Internet of Things) is used to optimize processes, monitor equipment performance, and improve operational efficiency. IIoT enables predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and automation, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
Smart Cities and Infrastructure Management:
IoT enables cities to become smarter by monitoring and managing critical infrastructure such as transportation systems, energy grids, waste management, and public safety. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced quality of life for citizens.
Agriculture and Precision Farming:
IoT sensors and devices are used in agriculture to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. This data-driven approach enables farmers to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to higher crop yields and reduced environmental impact.
The Benefits of IoT:
The widespread adoption of IoT(Internet of Things) brings several significant benefits across industries.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity:
By automating processes and enabling real-time monitoring, IoT enhances operational efficiency, reduces manual intervention, and improves overall productivity.
Enhanced Safety and Security:
IoT devices provide advanced security features, including surveillance systems, access control, and alarm systems, making homes, workplaces, and public spaces safer.
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization:
IoT enables optimized resource utilization by collecting and analyzing data. This leads to cost savings through efficient energy consumption, streamlined logistics, and predictive maintenance.
Data-Driven Insights and Decision Making:
IoT generates vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to gain valuable insights. This data-driven decision-making empowers businesses to respond quickly to changing conditions and make informed choices.
Challenges and Concerns:
While IoT(Internet of Things) presents enormous opportunities, it also poses certain challenges and concerns.
Security and Privacy Risks:
With the interconnected nature of IoT, security vulnerabilities can expose sensitive data and systems to cyber threats. Robust security measures must be implemented to protect against hacking and data breaches.
Interoperability and Standardization:
IoT devices from different manufacturers may use proprietary protocols, creating interoperability issues. Standardization efforts are crucial to ensure seamless integration and communication between devices.
Scalability and Network Congestion:
As the number of IoT devices increases, scaling up networks becomes critical. Network congestion and bandwidth limitations need to be addressed to accommodate the growing IoT ecosystem.
Ethical and Social Implications:
IoT raises ethical concerns related to data privacy, consent, and the potential for surveillance. Balancing technological advancements with ethical considerations is essential for responsible IoT deployment.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success:
Addressing the challenges associated with IoT requires proactive measures and careful planning.
Robust Security Measures:
Implementing encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms are crucial to protect IoT devices and networks from cyber threats.
Interoperability Standards:
Standardizing communication protocols and data formats is essential to enable interoperability between different IoT devices and platforms.
Reliable and Scalable Connectivity:
Investing in robust connectivity infrastructure, such as 5G networks and edge computing, ensures reliable and high-speed communication between IoT devices.
Ethical and Responsible Implementation:
Adhering to privacy regulations, obtaining user consent, and transparently managing data are essential to address ethical concerns associated with IoT.
The Future of IoT:
The future of IoT looks promising, with several emerging trends shaping its trajectory.
Edge Computing and Fog Computing:
Edge computing brings processing power closer to IoT devices, reducing latency and enabling real-time data analysis. Fog computing extends this concept further by distributing data processing across multiple edge devices.
5G and IoT:
The rollout of 5G networks provides higher bandwidth, lower latency, and increased device density, unlocking new possibilities for IoT applications that require ultra-fast and reliable connectivity.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms with IoT devices enables intelligent data analysis, predictive maintenance, and personalized user experiences.
Blockchain and IoT:
Blockchain technology enhances the security and transparency of IoT by providing tamper-proof data storage, decentralized authentication, and secure peer-to-peer transactions.
The Role of Big Data in IoT:
This section explores how big data plays a crucial role in IoT. It covers topics such as data collection and analysis, highlighting the importance of processing the massive amount of data generated by IoT devices. It also discusses data storage and management techniques and emphasizes the significance of real-time decision making based on the insights derived from IoT data.
IoT and Energy Efficiency:
This heading focuses on the impact of IoT on energy efficiency. It discusses how IoT enables smart energy management systems, allowing for optimized energy consumption in various settings. Topics such as demand response and peak load management are explored, along with energy conservation practices in buildings through IoT technology.
IoT and Wearable Technology:
This section highlights the intersection of IoT and wearable devices. It delves into the applications of IoT in wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and health monitoring devices. It also explores the role of smartwatches and connected accessories in enhancing user experiences and performance tracking in sports.
IoT in Supply Chain and Logistics:
This heading discusses the application of IoT(Internet of Things) in supply chain management and logistics. It covers topics such as inventory management and tracking, highlighting how IoT enables real-time visibility of goods throughout the supply chain. It also explores how IoT facilitates fleet management, route optimization, and automation in warehouses.
Privacy and Data Protection in IoT:
This section addresses the important topic of privacy and data protection in the context of IoT. It discusses the collection of personal data by IoT devices and emphasizes the need for user consent. It also explores privacy regulations and compliance requirements that organizations should adhere to, along with the challenges of balancing convenience and privacy concerns.
IoT and Environmental Sustainability:
This heading focuses on how IoT contributes to environmental sustainability. It explores topics such as smart grids and energy conservation, showcasing how IoT enables efficient energy management and reduced carbon footprint. It also discusses environmental monitoring and conservation practices facilitated by IoT technology, along with its application in sustainable agriculture and smart irrigation.
IoT and Smart Transportation:
This section highlights the impact of IoT(Internet of Things) on transportation systems. It covers topics such as connected cars and intelligent traffic management, showcasing how IoT technology improves traffic flow and enhances road safety. It also explores the potential of autonomous vehicles and their role in transforming the future of transportation, along with optimizing public transportation systems through IoT innovations.
These additional headings provide more specific areas of focus within the broader topic of IoT, allowing you to dive deeper into various applications, challenges, and benefits associated with IoT technology.
Conclusion:
The Internet of Things is poised to transform our world, connecting devices, systems, and people in unprecedented ways. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT brings numerous benefits while presenting challenges that need to be addressed.
By adopting robust security measures, promoting interoperability, and embracing emerging technologies, we can unlock the true potential of IoT and create a future where connectivity and automation enhance our lives.
READ MORE
- Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam: The Missile Man of India
- Microsoft: A Dominant Player in the Technology Industry
- Nikola Tesla: A Look into the Mind of a Scientific Pioneer
- An Overview of Blockchain Technology:
- Why iPhone doesn’t support SD card?