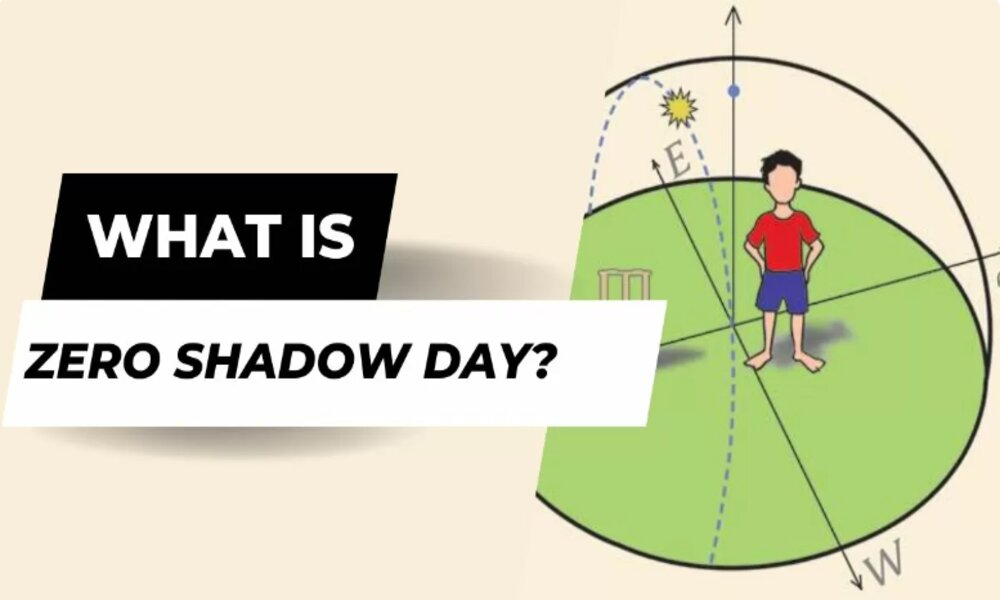
Zero Shadow Day is a fascinating astronomical phenomenon that occurs twice a year at specific latitudes on Earth, where the Sun’s position is directly overhead, and objects cast no shadows. This event has been known and observed for centuries, but it is still a wonder to experience it.
In this article, we will explore what Zero Shadow Day is, how it occurs, when it can be observed.
What is Zero Shadow Day?
Zero Shadow Day is a day when the Sun’s position is exactly at the zenith, or the point directly overhead, at a specific latitude. At this point, the Sun’s rays fall vertically on the Earth’s surface, making objects cast no shadows.
This phenomenon occurs twice a year, around the time of the equinoxes, when the Sun is directly over the equator. On these days, the Sun’s rays are perpendicular to the Earth’s surface at the equator, resulting in no shadows.
How does it occur?
The Zero Shadow Day phenomenon occurs due to the Earth’s tilt and its rotation around the Sun. The Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun. This tilt causes the Sun’s rays to hit different parts of the Earth at different angles throughout the year, resulting in different seasons.
Around the time of the equinoxes, the tilt of the Earth’s axis is such that the Sun’s rays are perpendicular to the Earth’s surface at the equator. This means that there is no angle between the Sun’s rays and the objects on the Earth’s surface, resulting in no shadows.
Where and when can it be observed?
Zero Shadow Day can be observed at specific latitudes on Earth where the Sun’s position is directly overhead. These latitudes are known as the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, which are located at approximately 23.5 degrees north and south of the equator, respectively. The Tropic of Cancer is located in the Northern Hemisphere, while the Tropic of Capricorn is located in the Southern Hemisphere.
Zero Shadow Day occurs twice a year at these latitudes, around the time of the summer and winter solstices. The summer solstice occurs around June 21, and the winter solstice occurs around December 21. On Zero Shadow Day, the Sun’s position is directly overhead at solar noon, which is when the Sun is at its highest point in the sky.
Conclusion:
Zero Shadow Day is a fascinating astronomical phenomenon that occurs twice a year at specific latitudes on Earth. It occurs around the time of the equinoxes, when the Sun’s position is directly overhead at the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, resulting in no shadows.
This event has cultural significance in many parts of the world and is celebrated as a holy day or an auspicious time for planting or spiritual renewal. While this phenomenon may seem like a small event in the grand scheme of things, it serves as a reminder of the wonder and complexity of our planet and the universe beyond. It is a moment worth witnessing and appreciating for its natural beauty and cultural significance.
READ MORE
- Understanding Dopamine
- Jesus Christ: A Living Presence in the Lives of Believers
- Which is the main mineral used to make aluminum?
- Good Friday and Easter: A Day of Reflection and Remembrance
- World Food Day: Understanding the Importance of Sustainable Food Systems
- Earth Day: Celebrating Our Planet and Taking Action for a Sustainable Future
- The Red Fort: A Cultural Icon of India’s Rich Heritage and Significance
- Exploring the Wonders of Ellora Caves: A Marvelous Fusion of Art, Culture,
- संपादन तकनीक में संपादकीय चिन्ह और पांडुलिपि संशोधन, प्रूफ संशोधन