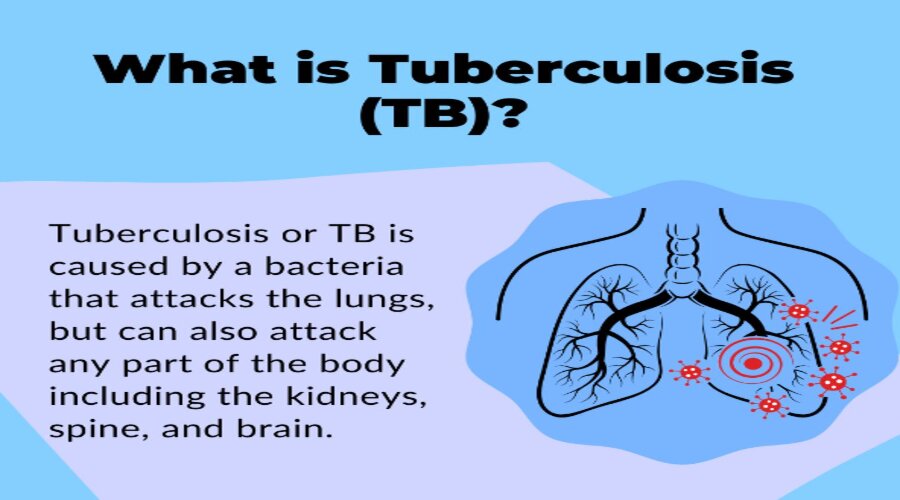
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB mainly affects the lungs but can also infect other parts of the body, such as the spine, kidneys, and brain. TB is a contagious disease that spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
It is a global health problem that affects millions of people every year, particularly in low and middle-income countries.
In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis.
Causes of Tuberculosis
TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a bacteria that can be spread from person to person through the air. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, they release tiny droplets containing the bacteria into the air. These droplets can then be inhaled by others, leading to infection.
TB is more likely to spread in crowded and poorly ventilated areas. People who have weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those undergoing chemotherapy, are also more susceptible to TB infection.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
The symptoms of TB can vary depending on the part of the body that is affected. TB that affects the lungs, which is the most common form of TB, can cause the following symptoms:
- Coughing that lasts for more than two weeks
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood or phlegm
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
TB that affects other parts of the body can cause different symptoms, such as back pain, joint pain, and urinary problems.
Treatment of Tuberculosis
TB can be treated with antibiotics. The most common antibiotics used to treat TB are isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Treatment usually lasts for six months or longer, depending on the severity of the infection.
It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before the treatment is over. If you stop taking the antibiotics too soon, the TB bacteria may not be completely killed, and the infection may return. Incomplete treatment can also contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant TB, which is much more difficult to treat.
Prevention of Tuberculosis
The best way to prevent TB is to avoid close contact with people who have the infection. If you are at high risk of TB infection, you may need to take preventive antibiotics.
Vaccination is also available to prevent TB. The Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine that is commonly used in countries with a high incidence of TB. The vaccine is not very effective in preventing TB in adults, but it can be effective in preventing severe forms of TB in children. BEST way to control TB Kindly contact to your doctor and took precaution, as soon as possible.
Other preventive measures include:
- Maintaining good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly
- Improving ventilation in living and working spaces
- Using masks or respirators in high-risk situations, such as healthcare settings
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol, which can weaken the immune system
Conclusion
Tuberculosis is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can be prevented and treated with antibiotics. If you think you may have TB or have been in close contact with someone who has the infection, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Preventive measures, such as vaccination and maintaining good hygiene, can also help to reduce the risk of TB infection. With proper treatment and prevention, TB can be controlled and eventually eliminated as a global health problem.
PLEASE CONTACT TO YOUR FAMILY DOCTOR FOR ANY PROBLEM.. THIS IS ONLY AWARENESS POST….
READ MORE
- World Health Day: Building a fairer, healthier world
- Earth Day: Celebrating Our Planet and Taking Action for a Sustainable Future
- The Hidden Dangers of Tapeworm Infection
- Pinworms: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
- Breast Cancer: Understanding the Disease and Finding a Cure
- World Cancer Day: Raising Awareness and Finding a Cure